Download the PHP package reshadman/file-secretary without Composer
On this page you can find all versions of the php package reshadman/file-secretary. It is possible to download/install these versions without Composer. Possible dependencies are resolved automatically.
Informations about the package file-secretary
Notice Before Usage
For new versions of Laravel use spatie/laravel-medialibrary. The funcionality is almost the same except that the same files are stored multiple times. As a recommendation if you want image resizing functionality use something like thumbor which is more stable, secure, configurable and fast.
Laravel File Secretary


Get rid of anything related to files in Laravel, This package handles all for you.
What does this package do?
-
Handles your public assets (.css, .js, .etc) you can use your CDN provider to serve the static assets. with a simple function call. For instance you can serve your static files through Rackspace CDN. After each deploy a new unique id is assigned to the path so the cached assets would be purged.
- Image manipulation and storage: Store all of your images in the cloud (based on Laravel Adapters, Rackspace, S3, minio etc.), The image resizing is handled with simple configuration. You define templates and then images are generated automatically. Once a new image template created, you can use the nginx directives included in the package to remove the participation of PHP in next calls. Read the documentation for more info. A simple, fast and reliable method to manipulate images that are stored in the cloud.
- Detects redundant files, File names are generated based on the filesize + a hash function. so redundant files could not exist technically, You can implement your own file name generator, too.
- Storing files with a simple method call. They can be served without the participation of PHP, and they can be addressed with the package's helper functions if they are public.
- Database Tracking (Optional), Centerialized Eloquent model which tracks your stored files(and images), You can store files/resiable-images and attach them to your bussiness models. Then you can use them. If it is an Image the templates are accessible by simple getters in the model.
- Simple helper functions for dealing with resizable image urls, file urls, asset urls etc.
- A Simple controller for serving private/public files Serve both resizable images, and files. You can implement your own access control for restricting access on request. So for instance if the file should be only served to its uploader, you can implement an access controller which checks that the requested file is attached to the user model or not.
Getting Started
- Does this package fit my needs?
- Installation
- Configuration
- Usage
- Terminology : read for faster understanding.
- Defining Contexts
- Using the asset uploader
- Storing files
- File names
- Storing Service(Command)
- Storable file with file path
- Storable file with file content
- Storable file with file instance
- Storable file with file HTTP url
- Storable file with base64 encoded content
- Stored File Resoponse
- Storing images
- Deleting files
- Updating files
- Manipulating images
- Image Templates
- Using the dynamic generic template
- Writing your own template
- Storing manipulated image
- Storing Eloquent-tracked files
- When to use tracked files
- Storing simple files and manupulateable images
- Storing manipulatable images
- Using your own model
- Deleting Eloquent-tracked files
- Handle what happens on delete
- Serving files
- Default Routes
- Restricting access
- Serving public files and manipulated images
- Serving images without the participation of PHP
- Helper functions
- Nginx Directives And Production Notes
Does this package fit my needs?
https://12factor.net offers some practical specs for dealing with files, called attached resources. As files are an important part of the most of the information systems, they should be stored in a reliable, fast third party service (Like Amazon S3, or Rackspace object storage).
This package is an implementation of an spec for making Laravel application 12factor compatible for attached resources. You can follow the spec with your own implementation.
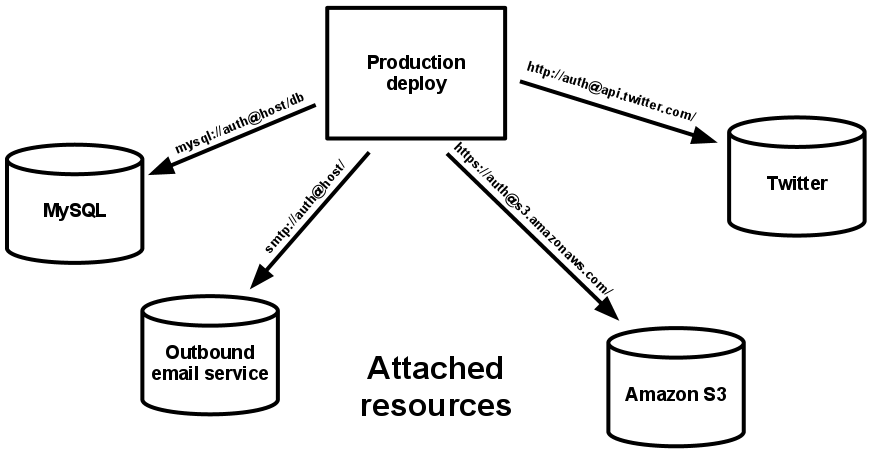
So if your application domain is not about files (You are not Dropbox or Amazon S3 itself :D). You can follow the spec and use the features this package offers, There are typically some main usecases for files:
- Serving private/public files (Like PDF, Docs etc)
- Serving manipulatable images (Images that should be re-sized, watermarked etc), which is computation/memory heavy.
- Serving static assets (like css, js, svg) etc.
- Attaching and tracking business domain files to their equivalent business model (Like the profile image of a user)
Laravel file-secretary offers some simple solutions for the above needs. We did not apart the package to individual ones to respect the simplicity. The interface that this package offers could be much simpler and more performant as Laravel file-secretary has been developed periodically it is not in its simplest shape. We will keep that in mind for next releases.
Installation
Run the following command in your project directory, to add the package to composer.json:
Add the Service Provider to your config/app.php
Then publish the configuration file:
If you want to use the eloquent model for attaching files to your models, export the migration:
Configuration
Almost everything is handled by configuration, For understanding how this package works please read the documentation blocks in the default config file here:
Usage
The best way to see the usage is by reading the integration tests, however you may read the following doc to understand what it does.
Terminology
Contexts: file-secretary uses contexts for detecting where to store the files based on laravel filesystem drivers,
we have four context categories basic_file, image, manipulated_image and assets,
all contexts should have a laravel filesystem driver, and a folder name in the driver.
When you command to store the file in a context, the equivalent, laravel disk driver is found by the config
and the starting path(folder of the context) is considered as the directory. Also generating file URLs is handled by this config.
Context Category: basic_file: a basic file is a simple file that does not need
any manipulation, when defining contexts you can indicate a basic_file context,
and when you command to store the file, they will be added in the context's laravel filesystem
driver and the given folder. Files can be served with or without the participation of PHP.
Context Category: image: Images that should be manipulated and mutated based on your given config.
Storing manipulateable images is not different from storing simple files, except that
instead of a unique file name, they are stored in a unique directory,
so the main image and its manipulated children are always in that unique folder.
You can also have different context strategies for the main image and its manipulated children.
You can indicate that the manipulated images of the main image should not be stored at all or be stored
beside the main image, or be stored in a different context (as manipulated images are not critical they can
be stored in more cost effective storage like your own server).
Context Category manipulated_image: This is a context that is used for image context as the place
to store its manipulated images.
Context Category: asset: If you want, you can upload your entire built asset directory to your cloud CDN provider,
like Rackspace's public CDN.
Asset Folders/Tags: These are the folders that you want to upload to the cloud, in your blade templates
by calling fs_asset('assetFolderName', 'your_local_path_to.css') you can address them, assets are purged on each call, so the
browser won't serve the old versions.
Image templates: Templates are objects that keep the responsibility for mutating and manipulating images You may use the default generic template (which dynamically re-sizes, strips images with different config), or implement your own one. They are defined in the config.
Database/Eloquent Tracked Files: After storing a file in a context you may assign it to the centralized eloquent model, this model can be attached to other business models, like the profile image of a user.
File/Folder name: in the context of this package, a file name is a unique id
which is generated automatically, it needs to be unique in the context of your app.
You can implement your own file name generator. By default it is based on the sha1(fContent) + filesize, It guarantees
That the same file is not redundant in the context.
Serving Files/Images/Manipulated Images: Simply you may serve files publicly or privately, There is an HTTP endpoint in this package
which will serve the requested files/images, It retrieves the equivalent context and file_name from the requested URL,
and downloads the file from the storage of the found context and serves it to the user.
Before downloading, It calls the privacy object of the found context, if it returns false, it will throw an HTTP
400 Exception. You can define your privacy classes for the found context, which will be discussed in the documentation.
Defining Contexts
You can read the default config('file_secretary.contexts') element of the config file to see all the available
options for creating contexts.
Context must be unique in terms of Laravel filesystem disks + the starting folder in the disk (the
context_folder).
Using the asset uploader
To serve your static assets through a public CDN, like Rackspace public CDN, you create an asset context like below:
Other things will be handled automatically, in development environment, the assets will be served
local and in production env they will be served from the given driver_base_address
To sync the latest assets run:
To address the assets in the template call:
To delete the old versions:
By default the last two version are kept, and other versions are deleted after a successful upload.
For a different strategy you may change the following event listener in file_secretary.php:
Storing Files
file-secretary takes care of storing files after they have been validated by you. Then they can be tracked and served.
You can pass different file targets to the store command. For storing a file you should create an instance of the following class:
To see the list of available file targets read the contents of the above class.
The
PresentedFileclass support different file types inluding: URL, File Path, File Content and File Instance ,read the following docs.
File names
You can not control the file names, they are used for tracking files and images.
For the files of a basic_file context, the storing format would be something like this:
For the files of a image or manipulated_image context the file name would be some thing like this:
You can define your own unique id generator in the config:
Please note that your closure should always return a unique string.
The function prevents redundant files in the same context.
Storing command
After you have created the PresentedFile instance you should pass it to the store command.
For knowing all the constructor parameters of the PresentedFile class read the class implementation.
For finalizing the storage read the following:
Storable file with file path
If you have the a local file path, you can create the PresentedFile instance like the following:
Storable file with file content
If you have the file content, you can create the PresentedFile instance like the following:
Storable file with file instance
If you want to store the file from an instance of request UploadedFile or a Symfony file instance
read the following
Storable file with file HTTP url
If you want to store a file from a URL you can read the following:
Storable file with base64 encoded content
If you want to store a file from a base64 string read the following:
Note that if other meta data is attached to the string it should be removed by you, the mime type will be detected automatically.
Stored File Response
After executing the store file command it will return an instance of:
for knowing methods read the class implementation.
Storing Images
Storing images is not different from storing files. You should only pass the proper
context_name which has image category to the PresentedFile instance.
new PresentedFile( 'context_name', '/path/to/file', PresentedFile::FILE_TYPE_PATH, "optional_original_file_name.pdf" );
Deleting files
To delete a file you should use the following service command:
If your deleting an image context and it stores templates, the manipulated images with be deleted, too.
Updating files
When dealing with cloud file storages, which some of them offer CDN services, it is not a good idea
to update a file, you can simply delete the old one and create a new one, that is because it takes some times
that the CDN provider fetch the new version for all edges. And because we do not focus on file names
in our implementation it is better to leave the file in the storage, or add a X-DELETE-AFTER header to that,
or delete it entirely and create a new file.
If you have some reason that this functionality is needed please create a PR or open an issue.
Please not that if you implement your own update strategy, do not use the built in file name generator function, because the file name is based on file content, so if you change the file content with the same file name, it will be overridden next time the old file is uploaded to the context.
Manipulating images
After you have created a context with category , image
file-secretary allows to manipulate and mutate images based on image templates,
you define image templates in the config file, and when the image is requested through the url
with predefined parameters, the main parent image is fetched from the disk storage, the image content
is passed to the template object and the template's result is served to the user.
The image templates are defined for all image contexts.
Image templates
To define your image templates you should add your config to the available_image_templates of the config file:
Using the dynamic generic template
By using the following class as the parameter of your image template config, you can control the behaviour with args, this will cover most of your needs:
The class parameter is the template implementation, each template can have some arguments,
the DynamicResiableTemplate get some arguments which allow you to satisfy most of your needs.
for resizing:
- Width: can be null or an integer, if null it will be automatically calculated
- Height: can be nul or an integer, if null it will be automatically calculated
- encodings: can be null or an array of images extensions like
['png', 'jpg', 'svg'], if null the same encoding as the parent image will be used. - quality: takes an integer from 1 to 100
- strip: when true and using imagick the embedded ICC profile of the image can removed, this reduces the generated image size significantly, the ICC profile is used to generate same true colors on different displys.
- mode: You can use different fit strategies take a look at template manager class (public_images``` section of the config file.
Serving public files and manipulated images
If you have public contexts, you can use the driver_base_address functionality to remove the participcation of PHP
for basic_file context category, the base address will be prepended to the relative path, and it will be served
directly.
Serving images without the participation of PHP
for image context category, the main image is always served from the base address, however the image templates
are still served from PHP, you can create an Nginx reverse proxy which does one of the following:
-
Set
store_manipulatedtotrue, Create an Nginx directive that will call the laravel endpoint on file not found of the base address, the laravel endpoint will store the file beside the main so the in the next call the image is served from your upstream base address. -
Set
store_manipulatedtofalseUse a reverse proxy with caching, which calls the laravel endpoint, after a successful call Nginx will cache the image, so the image will be served from Nginx's cache. -
Set
store_manipulatedto another context which uses a local disk, set the disk path as root for Nginx and on 404, call the laravel endpoint, or make the route path and disk path look the same, So it will be routed to the generator controller automatically when the file does not exist.Nginx Directives will be added to the package soon. To make it much more simpler.
Helper functions
Will be added soon.
Nginx Directives And Production Notes
Will be added soon.
Running the Integration Tests
There are integration tests written for this package. To run integration tests do as the following:
-
Create your
phpunit.xmlfile based on the packages'sphpunit.dist.xml:cp phpunit.dist.xml phpunit.xml - Fill the phpunit config with your environment variables.
The package has been tested with Rackspace Object storage, to prove the
functionality in cloud. You can change the
phpunit.xmlfile and the configs infixtures/config/to integrate them with your testing environment. - Run the tests with
vendor/bin/phpunit --debug
Currently there is no isolated object unit testing for this package. They will be added in next releases.
Package Roadmap
- Writing more integration tests + isolated object unit tests.
- Use more semantic names for features, class names and methods names.
- Make the tracking, eloquent independent.
- Refactor the code both for design and performance.
- In a new release, use a polymorphic model for database tracked files which allows to indicate that whether a file has been used somewhere in the other models or not (by design). Which in result we can delete unused tracked files. This also works only with SQL databases.
- Adding Nginx Directives
- Delegate some works to worker queue.
About the package
This package has been extracted from jobinja.ir - The leading job board and career platform in Iran, This is part of the work for making jobinja.ir, 12factor.net compatible.
License
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.
All versions of file-secretary with dependencies
ramsey/uuid Version >=3.7 <3.8.0
guzzlehttp/guzzle Version ~5.3|~6.0
adrienrn/php-mimetyper Version 0.2.0
intervention/image Version >=2.4.0 <2.5.0


